High Purity 5n Germanium metal
| Group | 14 | Melting point | 938.25°C, 1720.85°F, 1211.4 K |
| Period | 4 | Boiling point | 2833°C, 5131°F, 3106 K |
| Block | p | Density (g cm−3) | 5.3234 |
| Atomic number | 32 | Relative atomic mass | 72.630 |
| State at 20°C | Solid | Key isotopes | 73Ge, 74Ge |
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d104s24p2 | CAS number | 7440-56-4 |
Uses and properties
Germanium was used in early transistors similar to the one featured here.Appearance A silvery-white semi-metal. It is brittle.
Uses
Germanium is a semiconductor. The pure element was commonly doped with arsenic, gallium or other elements and used as a transistor in thousands of electronic applications. Today, however, other semiconductors have replaced it.Germanium oxide has a high index of refraction and dispersion. This makes it suitable for use in wide-angle camera lenses and objective lenses for microscopes. This is now the major use for this element.Germanium is also used as an alloying agent (adding 1% germanium to silver stops it from tarnishing), in fluorescent lamps and as a catalyst.Both germanium and germanium oxide are transparent to infrared radiation and so are used in infrared spectroscopes.
Biological role
Germanium has no known biological role. The element is non-toxic. Certain germanium compounds have low toxicity in mammals, while being effective against some bacteria. This has led some scientists to study their potential use in pharmaceuticals.
Natural abundance
Germanium ores are very rare. They are found in small quantities as the minerals germanite and argyrodite.Germanium minerals are also present in zinc ores, and commercial production of germanium is carried out by processing zinc smelter flue dust. It can also be recovered from the by-products of combustion of certain coals.
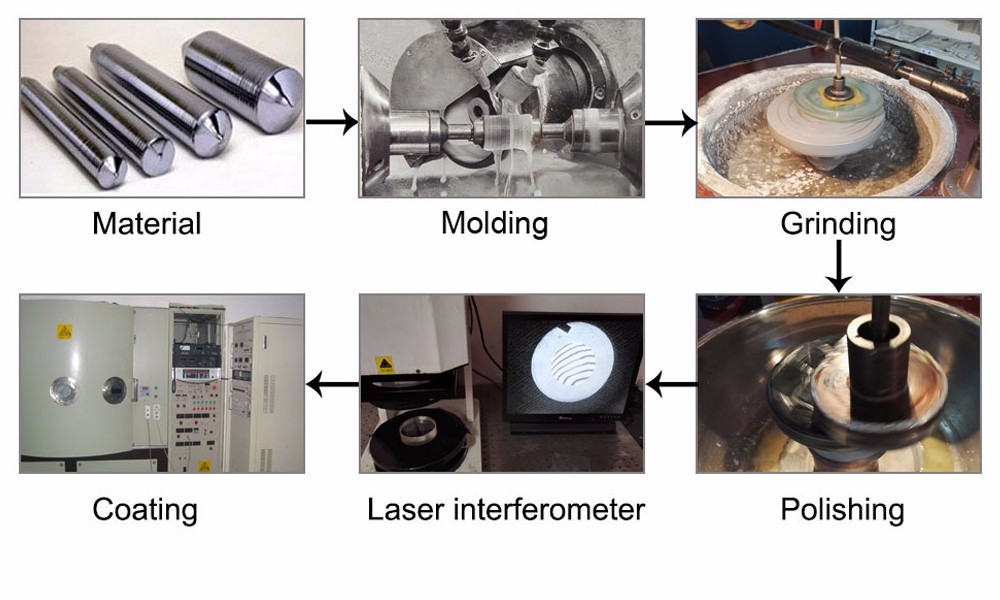
Product Description Single Crystal Germanium Lens
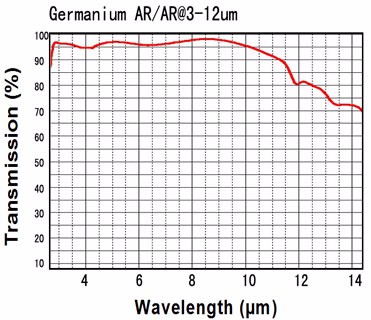
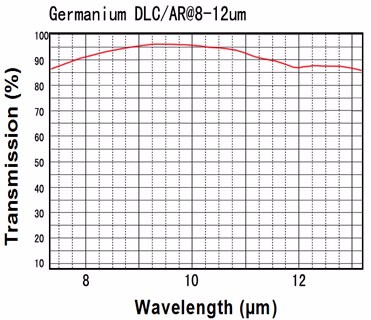
Germanium is used widely for lenses and windows in thermal imaging, FLIR applications, as germanium viewports. Its high index of refraction (about 4) makes it of particular interest. Useful transmission range of Germanium windows is from 2 to 13µm. Germanium is opaque in the visible.
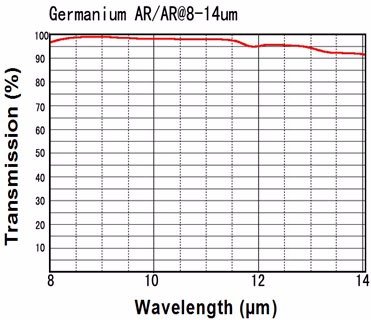
Custom germanium windows ,lenses and prisms are available in any size and configuration. Anti-reflection coatings can be applied for 2-14µm or 8-12µm (BBAR coating or DLC/BBAR) depending on your custom application.


|
Standard precision
|
High-precision
|
|
|
Dimension Tolerance
|
φ5-250mm+0/-0.2
|
φ3-350mm+0/-0.2
|
|
Thickness Tolerance
|
1-50mm+/-0.1
|
1-50mm
|
|
Centration
|
3 arc minute
|
1 arc minute
|
|
Surface Quality
|
60/40
|
20/10
|
|
Flatness
|
N<λ/2@633nm(at 50mm)
|
N<λ/10@633nm(at 50mm)
|
|
Clear Aperture
|
>90%
|
>95%
|
|
Chamfer
|
Protected <0.5mmx45deg
|
Protected <0.5mmx45deg
|

|
Germanium properties
|
|
|
Chemical Formula
|
Ge
|
|
Crystal Form
|
Poly or Single Crystal
|
|
Crystal Class
|
Cubic
|
|
Resistivity, Ohm*cm
|
5-40
|
|
Lattice Constant, Å
|
5.66
|
|
Molecular Weight
|
72.60
|
|
Density, g/cm3 at 300 K
|
5.33
|
|
Dielectric Constant for 9.37 x 109 Hz at 300 K
|
16.6
|
|
Melting Temperature, K
|
1210
|
|
Thermal Conductivity, W/(m K) at 293 K
|
59
|
|
Thermal Expansion, 1/K at 298 K
|
6.1 x 10-6
|
|
Specific Heat, cal/(g K) at 273-373 K
|
0.074
|
|
Debye Temperature, K
|
370
|
|
Bandgap, eV
|
0.67
|
|
Solubility in water
|
None
|
|
Knoop Hardness, kg/mm2
|
800
|
|
Mohs Hardness
|
6.3
|
|
Young’s Modulus, GPa
|
102.66
|
|
Shear Modulus, GPa
|
67.04
|
|
Bulk Modulus, GPa
|
77.86
|
|
Poisson’s Ratio
|
0.278
|